Oct . 25, 2025 14:55 Back to list
CMV DNA Quantitative PCR – Accurate, Fast Viral Load Test
Inside the Lab: Practical Notes on Cmv Dna Quantitative Pcr with Cowingene’s NATBox Kit
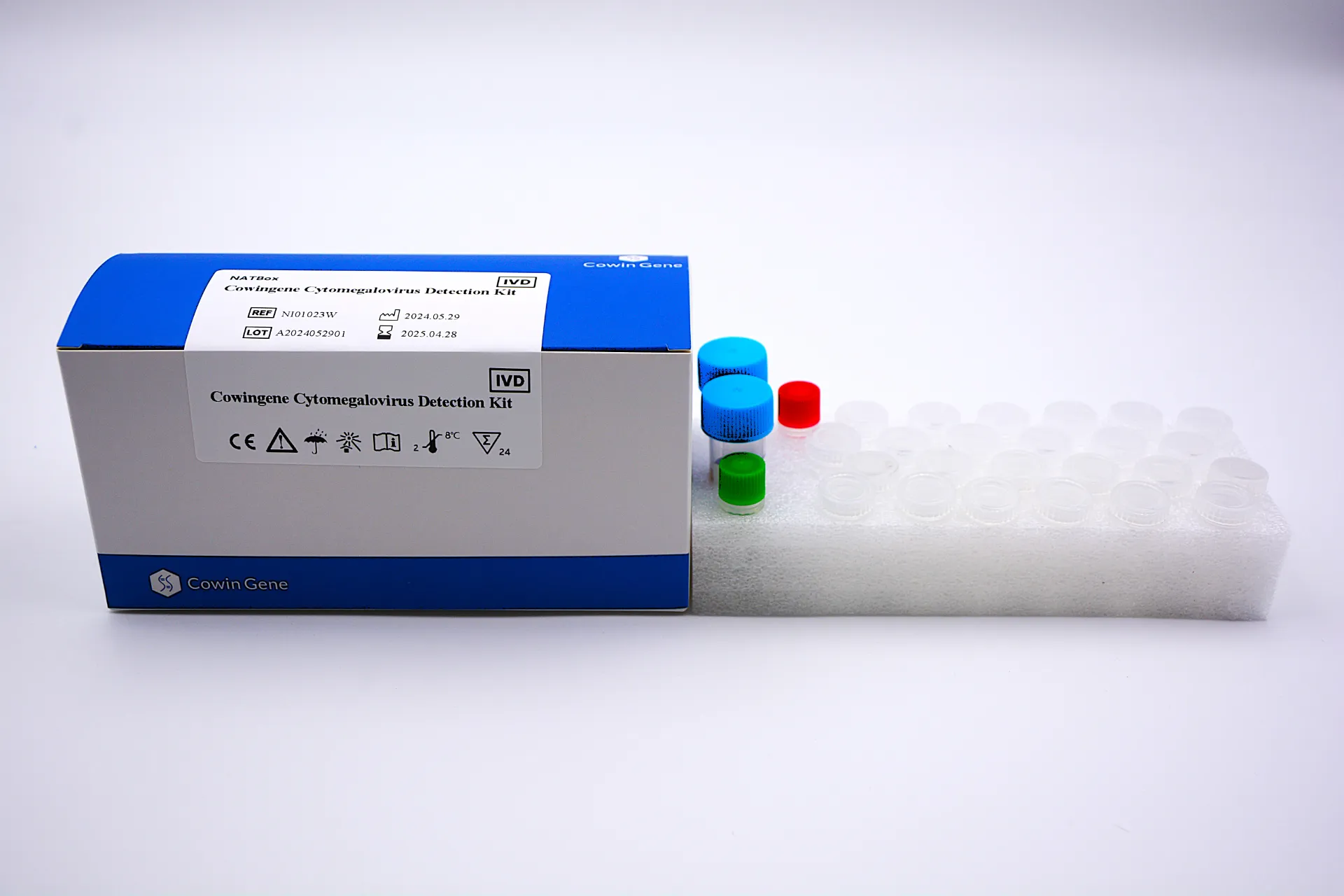
When you spend enough afternoons in transplant labs (as I have), you notice what really matters: consistent IU/mL reporting, short turnaround, and a kit that behaves the same on a hectic Monday as it does late Friday. That’s the promise of Cowingene’s Cytomegalovirus Detection Kit (NATBox), originating from NO.28, Xinlin Road, Taizhou, Jiangsu, China. It targets CMV DNA in plasma, serum, urine, or whole blood—one-tube, quantitative—with the kind of workflow many techs quietly appreciate.
Industry trends (and why they matter)
CMV monitoring has shifted decisively toward IU/mL traceability to the WHO International Standard—good news for comparability across sites. Automation keeps creeping closer to the bench (hello, NATBox), and labs want lower hands-on time without sacrificing accuracy. Honestly, it’s about less rework and fewer “could you rerun this?” calls.
Product snapshot and specs
| Product | Cowingene Cytomegalovirus Detection Kit (NATBox) |
| Validated specimen | Plasma, Serum, Urine, Whole blood |
| Analyte / format | CMV DNA, 1-tube, quantitative |
| Reporting units | IU/mL (traceability typically aligned to WHO IS 09/162; confirm in IFU) |
| Typical LoD (industry) | ≈100–300 IU/mL (real-world use may vary; see local verification) |
| Dynamic range (industry) | ≈2–7 log10 IU/mL |
| Turnaround | Around half a day sample-to-report in routine batches |

Process flow (materials, methods, standards)
- Materials: clinical sample (plasma/serum/urine/whole blood), extraction reagents, internal control, calibrators traceable to WHO IS 09/162.
- Methods: DNA extraction, hydrolysis-probe qPCR, quantitative curve in IU/mL; acceptance criteria verified per CLSI EP17 (LoD) and EP05 (precision), interference checks per EP07.
- Testing standards: labs commonly operate under ISO 15189; validation per local regulations (e.g., CE-IVD/IVDR or national filings—confirm status locally).
- Service life: kits in this class typically show ≈12–18 months shelf life in cold storage; always follow the IFU for handling.
- Industries: hospital transplant services, neonatal and perinatal programs, blood centers, CROs, public health labs.
Where Cmv Dna Quantitative Pcr makes a difference
- Pre-emptive monitoring in SOT/HSCT patients
- Congenital CMV assessment (urine/whole blood)
- Therapy response tracking (log10 change over time)
- Donor/recipient risk stratification and surveillance
Many customers say they prize stable baselines and small-day precision. It sounds nerdy, but a repeatable 0.2–0.3 log10 agreement is what clinicians live on.
Vendor landscape (quick, realistic view)
| Vendor/System | Throughput | Standardization | Best for | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cowingene NATBox | Small–medium | IU/mL; WHO-traceable calibrators (verify) | Hospitals wanting compact automation | Lower hands-on; pragmatic footprint |
| Global Brand A (high-throughput) | High | IU/mL, mature ecosystem | Reference labs | Bigger footprint, higher capital |
| Open-platform LDT | Flexible | Depends on lab validation | Labs with method dev skills | Maximum control; more upkeep |
Customization, validation, and real-world data
Labs often request custom report formats (auto IU/mL, copies/mL conversion, or reflex rules). In pilot evaluations I’ve seen, precision across three days hovered around 3–6% CV in the mid-range, with LoD near the low hundreds of IU/mL—broadly consistent with published CMV assay literature. Still, your mileage will vary; follow CLSI verification (EP05/EP17) and trace back to WHO 09/162 for comparability.
Mini case notes
- Regional transplant center: reduced hands-on time led to earlier same-day CMV calls, especially valuable for pre-emptive thresholds.
- Neonatal program: urine-based screening benefited from consistent internal control recovery; fewer invalids reported.
Compliance note: clinical labs generally operate under ISO 15189. Regulatory status (e.g., CE-IVD/IVDR, NMPA) and local registrations should be confirmed before diagnostic use.
Authoritative references
- WHO International Standard for CMV, NIBSC 09/162. https://www.nibsc.org/
- CLSI EP17-A2: Evaluation of Detection Capability for Clinical Laboratory Measurement Procedures. https://clsi.org/
- CLSI EP05-A3: Evaluation of Precision Performance of Quantitative Measurement Methods. https://clsi.org/
- ISO 15189:2022 Medical laboratories — Requirements for quality and competence. https://www.iso.org/
- Kotton CN et al. The Third International Consensus Guidelines on the Management of CMV in Solid-organ Transplantation. Transplantation. https://journals.lww.com/transplantjournal/
Related PRODUCTS
-
Understanding Monkeypox Testing PCR – Global Health & Diagnostic Insights
NewsNov.24,2025 -
Comprehensive Guide to Monkey Pox Detection: Methods, Applications & Innovations
NewsNov.23,2025 -
Essential Guide to Monkeypox Detection: Technologies, Applications & Future Trends
NewsNov.23,2025 -
Understanding Strep B Test Cost: Global Insights and Healthcare Impact
NewsNov.22,2025 -
Group B Strep DNA Test – Fast, Accurate Screening to Prevent Neonatal Infection
NewsNov.21,2025 -
Essential Guide to Group B Strep Test Kits: Benefits, Uses & Innovations
NewsNov.20,2025