Oct . 11, 2025 12:30 Back to list
HBV DNA Quantitative PCR Test – Fast, Accurate, Affordable
Real-World Notes on HBV DNA Quant: Field Impressions, Specs, and Buyer Tips
If you’ve spent any time in a virology lab, you know that getting hbv dna quantitative results right isn’t just a checkbox—it’s the backbone of treatment decisions, donor screening, and audit-proof quality control. I’ve seen labs struggle with turnaround, calibration drift, and reagent stability; honestly, the difference often comes down to kit design and how forgiving the workflow is during busy weeks.
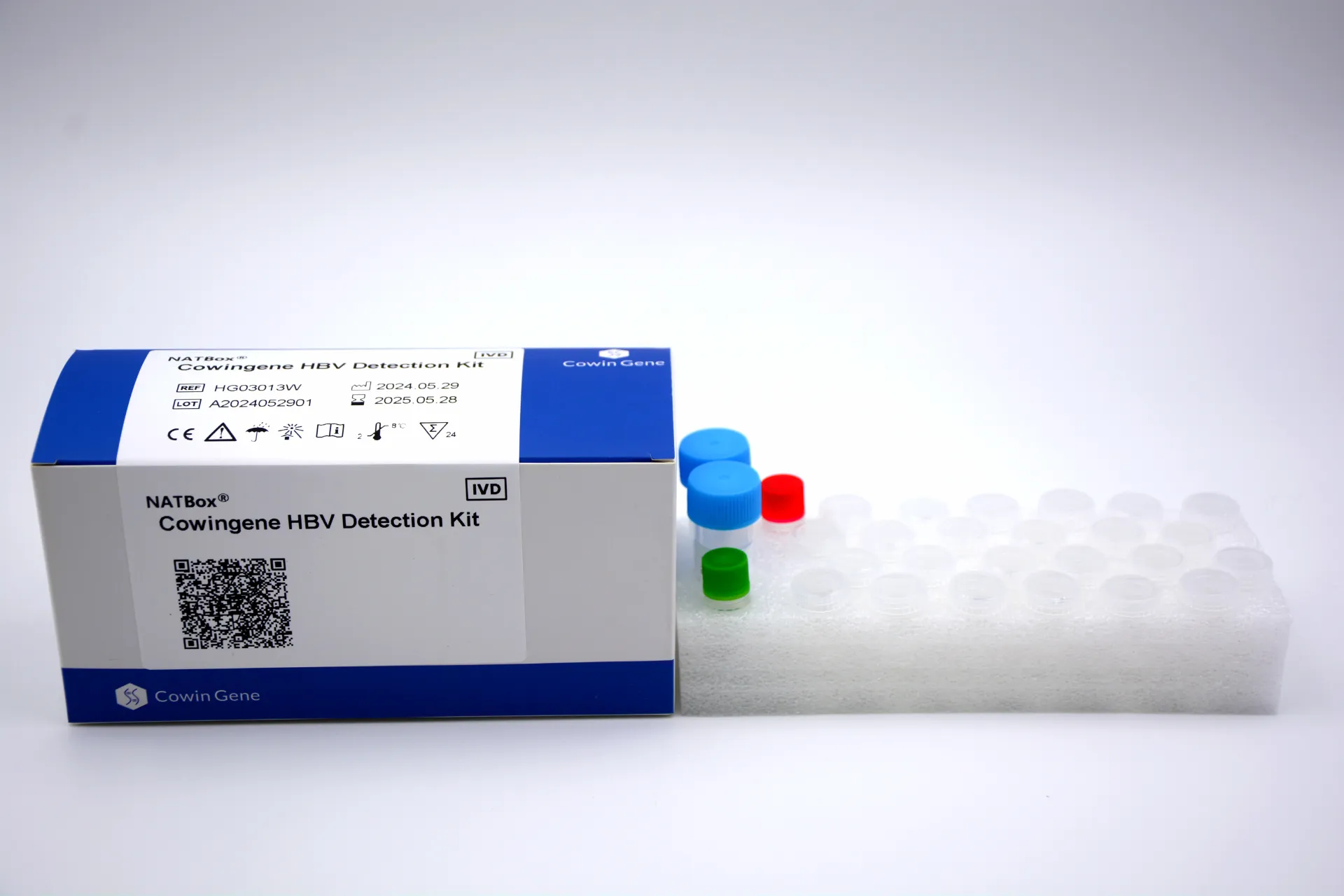
Product Snapshot: Cowingene HBV Detection Kit (NATBox)
Origin: NO.28, Xinlin Road, Taizhou city, Jiangsu Province, China. Validated specimen types: plasma, serum. Analyte: HBV via the NATBox system. It’s aimed at labs wanting reliable viral load with a compact footprint. To be honest, the simplicity is what caught my attention—less fiddly prep than some legacy platforms.
| Specification | Detail (≈ real-world use may vary) |
|---|---|
| Target | HBV DNA, quantitative PCR on NATBox |
| Validated specimens | Plasma, Serum |
| Reportable range | Typically from low tens of IU/mL up to ≥108 IU/mL (lab-verified) |
| Calibration/controls | External calibrators; positive/negative controls recommended per run |
| Shelf life (service life) | ≈ 12–18 months at 2–8°C (check label) |
| Throughput | Batch-friendly; throughput depends on NATBox configuration |
| Compatible industries | Clinical labs, blood banks, public health, CROs, pharma trials |
Why labs pick it
- Stable performance and straightforward workflows—less hands-on fiddling.
- Good fit for routine hbv dna quantitative monitoring in medium-throughput labs.
- Reasonable cost of ownership; reagents pack efficiently (that matters at scale).

Process Flow (Materials → Methods → QC → Release)
Materials: NATBox instrument, Cowingene HBV kit reagents, validated extraction (magnetic-bead or column), IVD-grade plastics. Methods: nucleic-acid extraction; real-time PCR targeting conserved HBV regions; dual-target internal control recommended. Testing standards: labs typically align with ISO 15189 for competence, CLSI MM06 for quantitative molecular assays, and WHO IU/mL traceability for reporting. QC: run controls every batch; verify linearity with multi-level panels. Service life: store kit at 2–8°C; avoid repeated freeze-thaw. Industries: clinical diagnostics, donor screening, surveillance programs.
Vendor Landscape (quick take)
| Vendor/Platform | Typical Use | LoD/Range (approx.) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cowingene NATBox | Routine hbv dna quantitative in mid-size labs | Low tens of IU/mL to high 108 IU/mL (kit/lab dependent) | Compact; cost-conscious; straightforward workflow |
| Roche COBAS systems | High-throughput reference labs | Vendor literature: very low IU/mL sensitivity | Automation powerhouse; premium pricing |
| Abbott Alinity/m2000 | Integrated molecular suites | Vendor literature: low IU/mL detection | Scalable; enterprise support |
Applications and Customization
- Clinical monitoring: trending hbv dna quantitative changes to inform therapy per guideline thresholds.
- Blood safety: NAT screening adjunct (policy-dependent).
- Trials/CRO: batch consistency, audit trails, IU/mL traceability.
- Customization: lab-specific extraction kits, LIS mapping, alternate control tiers, and bilingual reporting templates.
Field Feedback and Mini Case Notes
A regional hospital lab told me their switch shaved about 20% off prep time—nothing dramatic, but on Monday mornings that’s gold. Another site liked the linearity on diluted proficiency samples (around 102–106 IU/mL), saying it tracked “cleanly” against a reference assay. As always, confirm in your own verification: precision (CLSI EP05), linearity (EP06), and method comparison (EP09) before go-live.
Testing and Compliance Tips
- Use WHO IU/mL standards for traceability; document conversion factors.
- Follow ISO 15189 quality management; lock SOPs for extraction lots.
- Re-run controls when trending flags drift; keep Westgard-style charts.
- Report results with log10 IU/mL and uncertainty where applicable.
Note: Specifications and performance are subject to local validation and regulatory clearance. Always consult the IFU and your accreditation body.
References
- WHO. Guidelines for the prevention, care and treatment of persons with chronic hepatitis B. https://www.who.int
- EASL 2017 Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of hepatitis B virus infection. Journal of Hepatology.
- CDC. Hepatitis B Testing and Management Guidance. https://www.cdc.gov
- CLSI MM06—Quantitative Molecular Methods for Infectious Diseases, and related EP documents.
- ISO 15189:2022 Medical laboratories—Requirements for quality and competence.
Related PRODUCTS
-
Understanding Monkeypox Testing PCR – Global Health & Diagnostic Insights
NewsNov.24,2025 -
Comprehensive Guide to Monkey Pox Detection: Methods, Applications & Innovations
NewsNov.23,2025 -
Essential Guide to Monkeypox Detection: Technologies, Applications & Future Trends
NewsNov.23,2025 -
Understanding Strep B Test Cost: Global Insights and Healthcare Impact
NewsNov.22,2025 -
Group B Strep DNA Test – Fast, Accurate Screening to Prevent Neonatal Infection
NewsNov.21,2025 -
Essential Guide to Group B Strep Test Kits: Benefits, Uses & Innovations
NewsNov.20,2025